CSS
CSS, Cascading Style Sheets - is not a programming language, it is the code that styles web content (of the website built in a markup language such as HTML). In HTML every element on screen can be considered as a box. And box model is an essential term in CSS.
Each box has 4 areas: centrally located is content area (e.g. block of text, a table or an image) and around are padding area, border area and margin area.
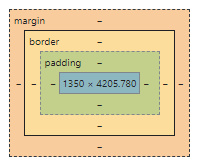
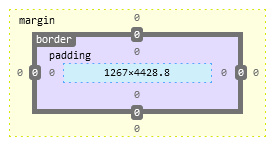
The source of both illustrations is www.kew.org. In MS Edge, Chrome and Opera you can find the left one; the right one is taken from Firefox. They differ only in colors (not in functions).
Each area is defined by a quite vast list of properties. CSS describes each element of the box giving it features such as color, size, positioning, relationships between elements in the document tree and so on. A set of such features is called stylesheet. From the programmer's point of view, a stylesheet consists of a list of rules. Each rule consists of two main parts: selector and a declaration block written inside curly braces (which has two parts: property name, followed by a colon (:), followed by a property value).
This is an example of valid code:
h1
{
background-color: black;
color: lime
}
It means: each first-level headers - h1 - in a document onscreen has black background with light green text (other features, like letters weight, are set in other rule).
In short: a CSS selector indicates (“selects”) the HTML element(s) you want to style, a declaration part defines its properties and gives them a specific value.